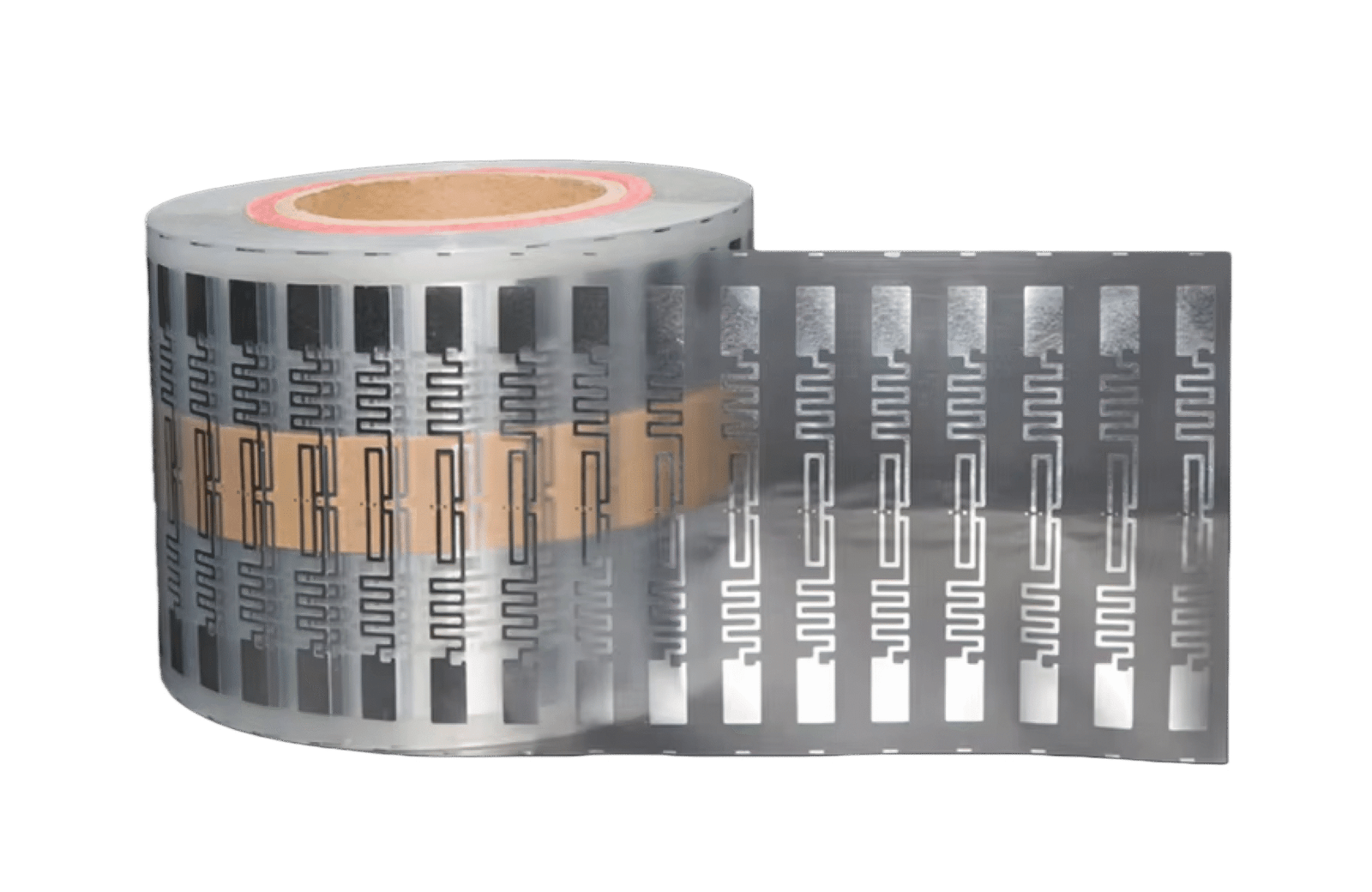
Description
Differece between RFID Wet Inlay and Dry Inlay
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology has become a cornerstone of modern tracking and identification systems. At the heart of RFID solutions are inlays, which combine a microchip and an antenna to enable wireless communication with RFID readers. These inlays are generally classified into two types: dry inlays and wet inlays. While both serve the same fundamental purpose, their manufacturing processes and physical characteristics make them suitable for different applications.

RFID Dry Inlays
Dry inlays are produced by attaching the RFID chip and antenna onto a substrate using a dry adhesive. Once the adhesive sets, the inlay is ready for further processing or integration into labels, cards, or packaging.
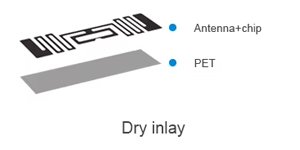
Key Characteristics:
- Thin and flexible: Ideal for applications requiring conformity to various surfaces.
- Easy to handle: The dry adhesive simplifies processing and integration.
- Moderate durability: Less resistant to harsh environments compared to wet inlays.
Applications: Dry inlays are widely used in inventory management, supply chain tracking, access control systems, and retail item tagging.
RFID Wet Inlays
Wet inlays are created by attaching the chip and antenna to a substrate with a wet adhesive, such as glue or adhesive film. They often undergo additional processing steps like lamination or encapsulation, which enhance their durability.

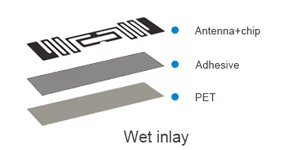
Key Characteristics:
- Moist adhesive layer: Provides immediate adhesion during manufacturing.
- Enhanced durability: Better suited for challenging environments due to protective layers.
- Stiffer structure: Offers more rigidity compared to dry inlays.
Applications: Wet inlays are commonly used in industrial asset tracking, outdoor equipment tagging, and automotive applications where resilience against environmental stress is essential.
Overview:
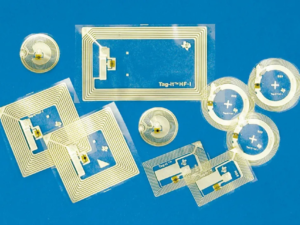
RFID Inlay are the essential functional element of an RFID tag, encoding identification data and transmitting it via radio frequency waves to readers and connected systems. Despite their tiny size- sometimes no larger than a grain of rice- they integrate seamlessly into countless applications.
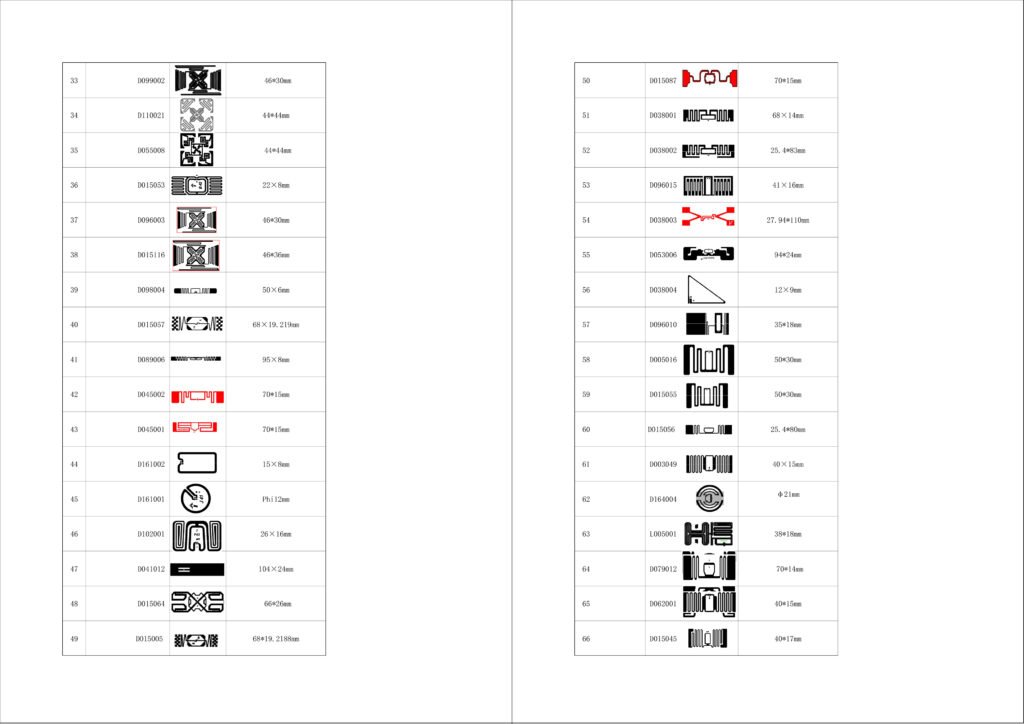
Each inlay is built from two key components:
Microchip (IC): Stores identification information
Antenna: A fine coil of aluminum, copper or silver wire that sends and receives RF signals.
These parts are mounted on a label and protected with a plastic layer. Depending on how they are applied, RFID inlays are classified as “wet” (with adhesive) or ” dry” (without adhesive).
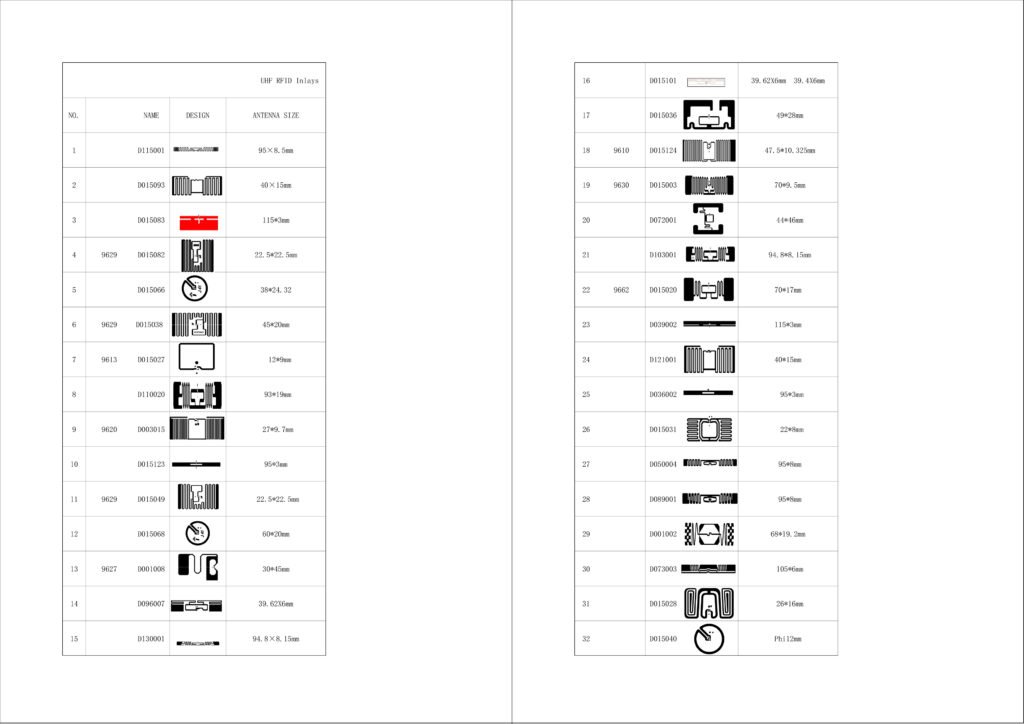
ReadFind delivers customized RFID solutions, offering a wide selection of inlays, labels and tags designed to meet your needs. We provide customized printing, diverse sizes, materials, and shapes, along with uniquely engineered antennas. Our encoding services include advanced data encryption, ensuring maximum security. With ReadFind, you’ll find the right RFID solution to streamline operations and strengthen your business performance.
Application:
Asset traclomg, Inventory, Appreal, Logistics, Library, Returnable Transport Units.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.